Difference Between Equity and Debt Mutual Funds

Difference Between Equity and Debt Mutual Funds
Here is a fact: the mutual fund industry in India has grown more than seven times in the past decade, and it stood at an Asset Under Management (AUM) of ₹74.40 lakh crore as of this June. A major portion of this growth is from fund categories such as equity and debt mutual funds. These two investment options present great opportunities for investors.
While both options help in achieving financial goals, they are quite distinct when it comes to risk, return, time horizon, and taxation. Hence, before investing, it becomes necessary to understand the equity vs. debt mutual fund concept.
In this article, we will examine what equity mutual funds and debt mutual funds are and how they differ from one another.
What is An Equity Mutual Fund?
An equity mutual fund is a type of mutual fund where the investment is primarily in stocks or other shares of a company. The goal of doing so is to create wealth through capital appreciation over time.
When you invest funds in an equity mutual fund, your investment is allocated alongside those of other investors into different companies on the market. In fact, the equity-oriented scheme held 59.7% of the industry's assets in 2024, while the debt-oriented scheme accounted for 14.8%.
Key Features of Equity Mutual Funds:
Equity mutual funds are a prominent choice of financial planning instruments due to the following features:
- Market-linked: Funds allocated into equity are tied to the market. The performance of the investments will depend on market performance. The returns are higher, but so are the risks.
- Diversification: Equity mutual funds can be invested in a variety of sectors, which helps mitigate risk through a robust investment strategy.
- Liquidity: A majority of equity mutual funds allow liquidity at any given time.
- Return Potential: Equity funds are known to offer higher returns compared to debt funds. However, the investments must be held for more than 5 years.
Types of Equity Mutual Funds
Based on the companies in which the funds are invested, their market capitalisation, and the investment style, equity funds can be classified into various types. Below are the different mutual fund categories:
- Large-Cap Equity Funds
- Funds are invested in the top 100 companies by market capitalisation.
- Quite stable compared to mid and small-caps.
- Most suitable for conservative equity investors.
- Mid-Cap Equity Funds
- Funds are invested in companies that rank between 101 and 250 on the S&P 500.
- The growth potential is quite high, along with high volatility.
- Appropriate for people with moderate risk profiles.
- Small-Cap Equity Funds
- Funds are invested in companies beyond the top 250 range.
- The growth rate is high, but the risk is equally high.
- Small-cap equity funds are great for long-term investors.
- Multi-Cap Funds
- Funds are invested across large, mid, and small-cap companies in a specified ratio stated by SEBI.
- It allows for diversification, thus offering stability alongside growth.
- Flexi-Cap Funds
- Funds can be allocated across any type, with the flexibility to change allocations.
- It is best suited for individuals who prefer to leave the allocation decision to the fund managers.
- Sectoral / Thematic Funds
- Funds are invested in specific sectors, including IT, Pharmaceuticals, and banking.
- The risk is higher as funds are in one industry.
- Best for investors who are willing to take the risk.
- Dividend Yield Funds
- Funds are allocated into dividend-paying stocks.
- Best suited for income-oriented investors.
- ELSS (Equity Linked Savings Scheme)
- This type of mutual fund investment comes with a 3-year lock-in period.
- A tax benefit can be availed of as per Section 80C (under the old tax regime).
- It is a good tax-saving and long-term investment option.
What is a Debt Mutual Fund?
A debit mutual fund is a type of mutual fund investment option that primarily invests funds in fixed-income securities. Funds are invested in options like government bonds, treasury bills, corporate debentures, and other money market instruments.
Debt mutual funds focus on stable returns instead of high capital appreciation.
Key Features of Debt Mutual Fund
Debt mutual funds are considered to be safer. Here are the other features:
- Diversification: They spread investments across different debt instruments like government securities, corporate bonds, debentures, and money market instruments, helping reduce risk and deliver more stable returns.
- Returns: The returns are stable and predictable but are relatively low compared to those of equity funds.
- Time Horizon: Debt funds are more suitable for short-to medium-term investments.
- Liquidity: Majorly liquid; however, some categories, like fixed maturity plans, have lock-ins.
- Risk: Debt funds carry a low to moderate level of risk. It is also subject to interest rates and credit risk.
Type of Debt: Mutual Fund
As per SEBI guidelines, debt funds are categorised depending on maturity and type of debt instruments:
- Liquid Funds:
- Funds are invested in instruments having a maximum 91-day maturity period.
- The risk is quite low.
- Money Market Fund:
- Funds are invested in instruments having a maximum 1-year maturity period.
- Offers good returns with low risk.
- Dynamic Bond Fund:
- The fund manager can adjust the maturity profile in accordance with the prevailing interest rate.
- Great for investors who prefer professional management.
- Gilt Funds
- Invest mainly in government securities only.
- There is no credit risk; however, there can be interest risk.
- Corporate Bond Funds
- At least 80% of the investment corpus is to be invested in high-rated corporate bonds.
- Best suited for investors with a low risk tolerance.
- Credit Risk Funds
- At least 65% of the funds must be invested in low-rated (below high-rated) corporate bonds.
- The returns are higher, but the risks are also higher.
- Short Duration Funds
- The maturity period ranges from 1 to 3 years.
- Ideal for investors with short to medium-term goals.
- Medium Duration Funds
- The maturity period ranges from 3 to 4 years.
- The risk and returns are balanced.
- Long Duration Funds
- Funds are invested in long-term bonds with a maturity period of 7 years or longer.
- The risk is quite high due to fluctuations in interest rates.
- Floater Fund
- Sixty-five per cent of the investment corpus is invested in floating-rate investments.
- The interest-rate risk is quite low.
Equity Mutual Fund vs Debt Mutual Fund: Key Differences
Both equity funds and debt funds are types of mutual funds, but they differ in so many ways. Below are the key differences that will help clarify the equity mutual fund vs debt mutual fund concept:
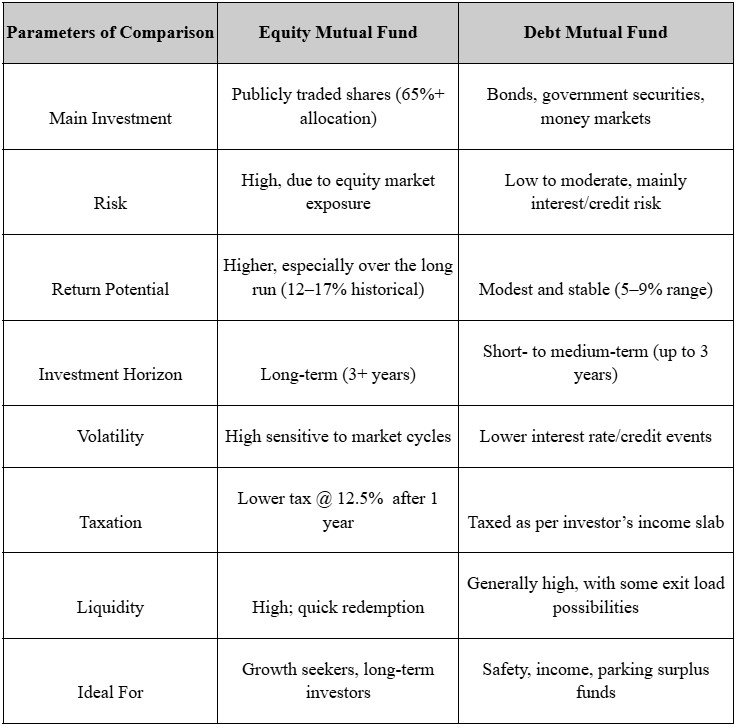
Equity vs Debt Funds: What to Choose?
If you are not sure which investment option will be apt for you, then here is a quick rundown:
Choose Equity if:
- Your financial goals may include wealth creation, retirement planning, or funding your child's education.
- Your risk tolerance is high.
- You can invest for more than 5 years.
Choose Debt if:
- You have short-term financial goals or require emergency funds.
- Your risk tolerance is low.
- The maximum period for which you can stay invested is 3 years.
Conclusion
When it comes to the most suitable investment option in terms of mutual funds, equity funds and debt funds have different purposes. Equity funds offer growth for your portfolio, whereas debt funds offer stability. The best choice is to create a balanced mix depending upon financial goals, time horizon, and risk profile. The right blend will ensure that wealth creation happens while being safe against market conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions - FAQs
What is the main difference between an equity mutual fund and a debt mutual fund?
Equity funds invest in company stocks for long-term growth, while debt funds invest in fixed-income securities, such as bonds, for stable income and capital protection.
Are returns from equity mutual funds guaranteed?
No. Returns depend on market performance.
Which mutual fund is better for beginners, equity or debt?
Beginners can start with hybrid funds, which combine both equity and debt, thereby balancing risk and stability.
Do interest rates affect debt mutual funds?
When interest rates are higher, the price of the bonds will fall, which can reduce debt fund returns. Conversely, falling rates benefit debt funds.
Get Expert Financial Advice
Book an introductory call with our Certified Financial Planner to explore how we can help you achieve your financial goals.
Book Your Appointment
