Key differences between Life and General Insurance
Imagine receiving an unexpected hospital bill, like the Kumar family, who suddenly faced over a lakh in medical expenses after a car accident, or the Sharma family struggling with the anguish of losing their primary income when the family's breadwinner passed away unexpectedly. Such real-life scenarios underscore the critical role of insurance in our lives.
Understanding the objectives of financial planning helps place both life insurance and general insurance in their rightful context. In this blog, you will learn about life insurance, general insurance, how they differ in plans, and more.
What is Life Insurance?
Life Insurance is an agreement between you and the insurance company.
It involves two main types of benefits: maturity and death benefits.
If you pass away during the policy term, the insurer pays a death benefit to your nominees, providing financial support in your absence.
Alternatively, if the policy matures, meaning it reaches a predetermined date with the policyholder still alive, a maturity benefit is paid out, which may be a lump sum or other specified financial amount.
Life insurance requires the policyholder to pay premiums regularly to the insurance company. In return, it offers financial security by eliminating uncertainty and providing monetary support when needed most, especially to dependents after the death of the breadwinner.
Life insurance is designed to protect individuals from two major risks in life:
- Imagine a sudden illness strikes a 35-year-old parent, leaving their young children and spouse without the financial security they once relied on. Dying too soon and leaving behind a dependent family without financial support is one of the greatest risks life insurance is designed to mitigate.
- Living too long without adequate income or financial resources for old age.
Life insurance is widely recognized as a financial tool that replaces risk with certainty and safeguards families during difficult times. It ensures that the policyholder or their nominee receives financial support when the insured event happens.
In India, life insurance has existed for over a century, yet its importance is still not fully understood by many. It serves as a vital financial protection system, offering both risk coverage and long-term benefits depending on the plan chosen.
In 2022, the life insurance penetration rate in India was approximately 3.2%, underscoring a significant protection gap and the need for greater awareness and education about the benefits of life insurance.
Objectives of Life Insurance
Life insurance aims to spread insurance protection nationwide, especially in rural areas and among socially and economically weaker sections. Its primary objective is to provide financial cover against death at an affordable cost to all insurable individuals.
It encourages savings by offering attractive insurance-linked investment options. These plans help mobilize public savings and channel them into secure and productive investments.
For more on how life insurance plans vary between pure protection and investment hybrids, check out our detailed guide on “ULIP vs Term Insurance”.
Life insurance operates with the responsibility of safeguarding policyholders’ funds. It invests these funds with a focus on safety, return, and national development, while serving both policyholders and the community.
Key objectives include:
- Offering financial protection and savings benefits.
- Acting as trustees of public funds.
- Providing efficient and courteous service.
- Adapting to changing social and economic needs.
- Ensuring responsible fund management.
- Promoting participation, dedication, and job satisfaction among employees and agents.
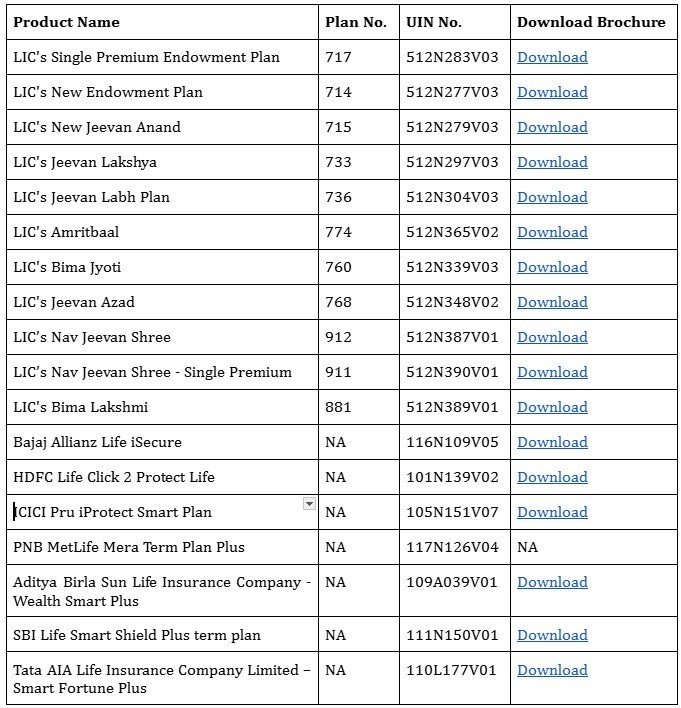
Life Insurance Plans
What is General Insurance
General Insurance is a contract between the policyholder and the insurer that provides financial protection against losses arising from assets such as health, property, vehicles, and businesses.
Unlike life insurance, general insurance does not cover life risks; instead, it provides compensation for specific losses, damage, or liabilities.
For instance, it can cover the costs of a car accident, a house fire, or theft from your business premises, helping maintain financial stability in the face of unforeseen events.
Timeline of General Insurance in India
1972
- The General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Act (GIBNA) was enacted.
- The Government of India took over 55 Indian insurance companies and 52 general insurers.
- General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC) was formed on 22 November 1972 under the Companies Act, 1956.
- GIC was created to control, supervise, and carry on general insurance business.
1973–1974
- Shares of all nationalised general insurance companies were transferred to GIC.
- After mergers, four companies remained as fully owned subsidiaries of GIC:
- National Insurance Company Limited
- New India Assurance Company Limited
- Oriental Insurance Company Limited
- United India Insurance Company Limited
1999
- The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act (IRDAA) came into force.
- GIC’s exclusive privilege in general insurance was removed.
2000
- GIC was designated as the national reinsurer.
- Its supervisory control over the four subsidiaries ended.
2003
- The General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Amendment Act, 2002, took effect on 21 March 2003.
- GIC ceased to be the holding company.
- Ownership of GIC and the four insurance companies was transferred directly to the Government of India.
Types of General Insurance
Health Insurance
This covers hospitalization, surgeries, illnesses, and daycare treatments. It offers financial protection against medical expenses. Common types of health insurance:
- Individual Health Insurance
- Family Floater Health Insurance
- Group Health Insurance
- Personal Accident Insurance
- Critical Illness Insurance
- Senior Citizen Health Insurance
- Maternity Health Insurance
When selecting health cover under general insurance, it’s vital to pick the right health insurance plan that aligns with your family’s needs.
Motor Insurance
Mandatory under the Motor Vehicles Act, it covers vehicles against accidents, theft, natural disasters, and third-party liabilities. Types of motor insurance:
- Car Insurance
- Two-wheeler Insurance
- Commercial Vehicle Insurance
- Third-Party Insurance (legally required)
- Comprehensive Insurance
Home Insurance
It protects the structure and contents of your home against fire, burglary, theft, or natural disasters. Key coverages: Structure, contents, burglary, and electrical damage.
Travel Insurance
This covers travel emergencies such as baggage loss, passport loss, trip delay, medical issues, and cancellation.
Commercial Insurance
Designed for businesses, it covers liabilities, property damage, and employee-related risks.
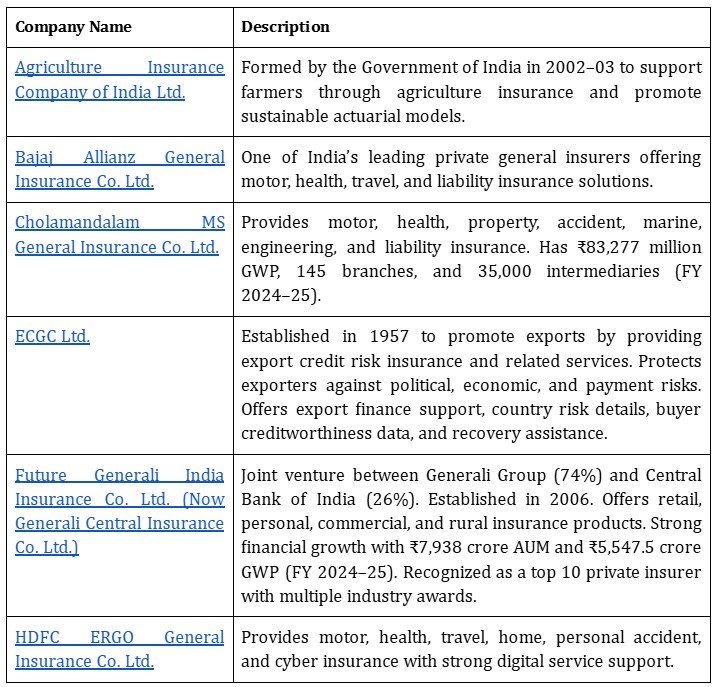
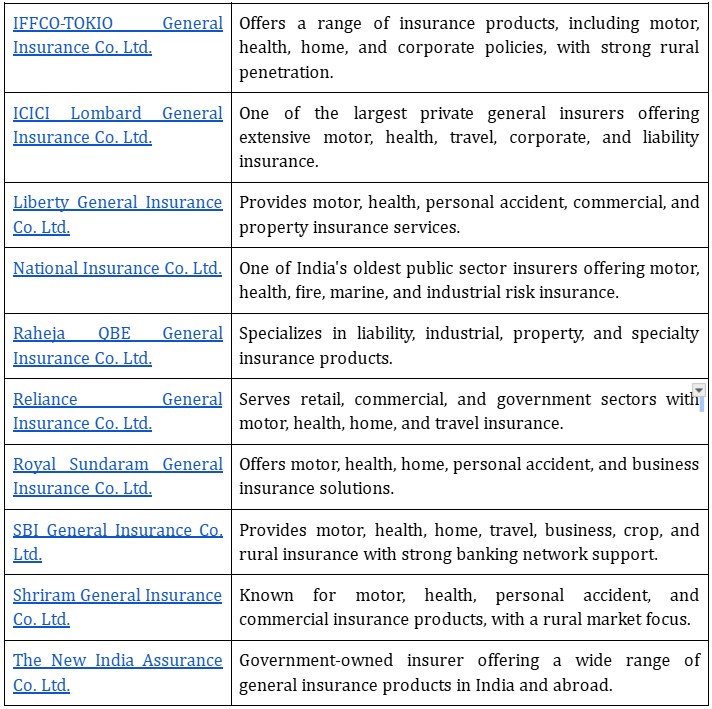
Major General Insurance Companies in India
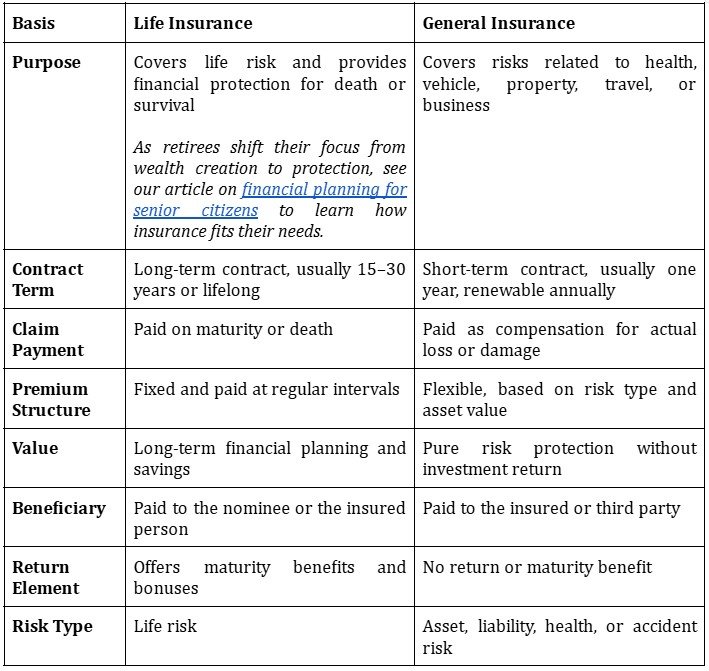
Life Insurance vs General Insurance: Key Differences
Life insurance protects income; general insurance protects assets.
By identifying which risk worries you most, you can take immediate action toward securing your financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions - FAQs
How do the premium structures and claim processes differ between life and general insurance?
Life insurance premiums are long-term and fixed, with claims paid on maturity or death. General insurance premiums are annual, risk-based, and paid as compensation for actual loss or damage.
What factors should individuals consider when choosing between life and general insurance products?
Individuals should consider purpose, duration, risk coverage, financial goals, premium affordability, claim process, and benefits. Life insurance provides long-term protection and savings, while general insurance protects assets, health, and liability risks.
What are the current trends in insurance penetration and product innovation in India?
Insurance in India is experiencing digital adoption, customized products, micro-insurance, growth in health and motor insurance, and increasing awareness. Penetration remains low but growing due to technology and government initiatives.
Get Expert Financial Advice
Book an introductory call with our Certified Financial Planner to explore how we can help you achieve your financial goals.
Book Your Appointment
